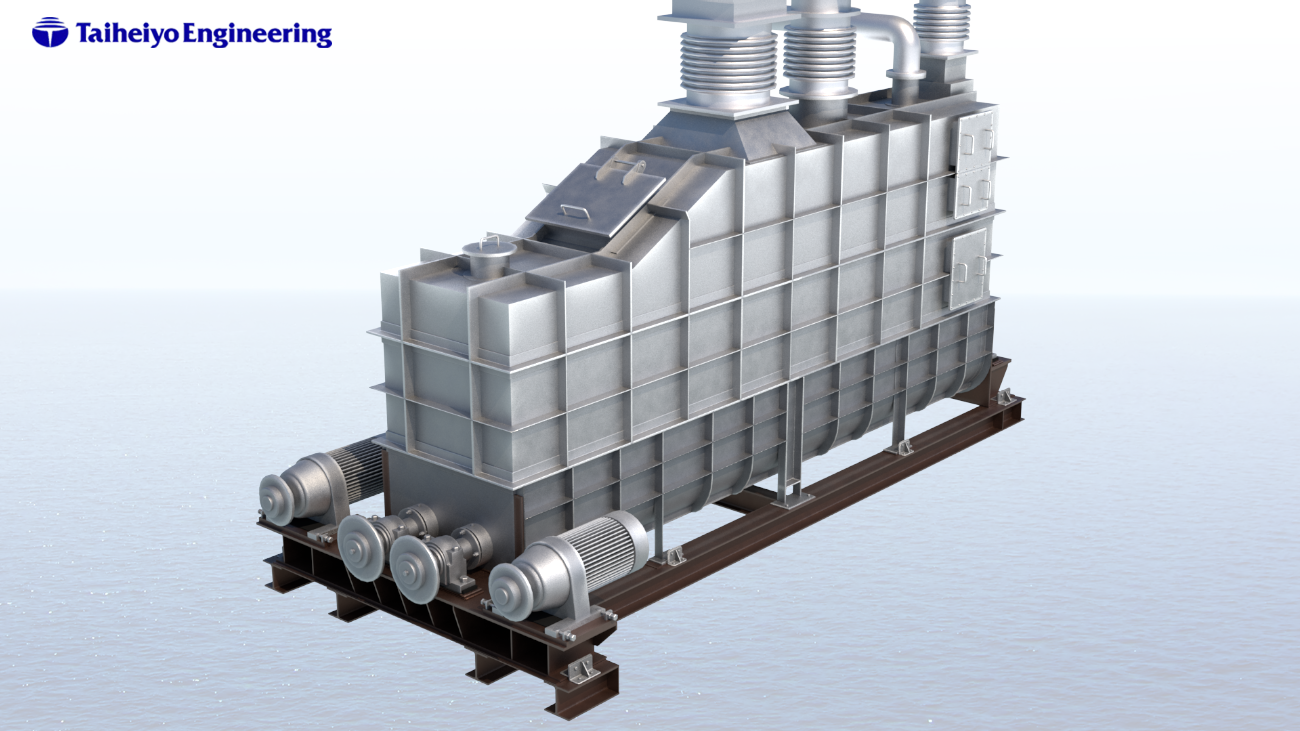
Sewage sludge contains a large amount of water but, after drying, a
considerable amount of combustible material and ash remains.
The cement industry can dispose of this
harmlessly and safely using high temperature waste heat and simultaneously utilize not only the
combustible material as fuel, but also the ash as raw material.
For the efficient utilization of sewage sludge, Taiheiyo Engineering Corporation and Taiheiyo Cement
Corporation have developed a breakthrough drying technology using the preheated raw meal.